Step-by-step guide to a successful CV
Introduction
The following sites will show you in detail how to compose a CV. The examples on each side are taken from the CV by Peter Hunzicker. Click on the picture below to get the full-sized CV to recheck while reading through the instructions. Click here for a pdf-version and a word document of this section.
Step 1: Heading

- Don’t write CV, curriculum vitae or résumé at the top. The recruiter can see what it is.
- Write your name in 14 point bold type so they can find you quickly in a
stack of CVs. - Don’t use German characters. Write Str. or Strasse.
- Use the English name for your city if there is one – Munich instead of
München. - Use the (+) sign instead of 00 before the country code for Germany (49).
International access codes differ. - Use a serious email address: badboy@gmx.de isn’t the image you want.
- Include your nationality.
- If you already have permission to work or study in
the country, say so. - For US applications, do not include your date of birth or age unless specifically requested.
- Do not include a photo unless you are applying for a job where appearance
matters such as acting or modeling.
Step 2: Objective

- Also called ‘career objective’, ‘job objective’ or ‘purpose’.
- It’s optional for CVs sent in response to a job opening because the objective should be this particular job.
- An Objective can be helpful if you are applying to a company that interests you, but not in response to a particular job opening.
- It isn’t necessary to write a full sentence.
- Make it short and specific. A vague, general objective (‘I want to contribute my outstanding communication and interpersonal skills and further develop them in a global company that is a leader in its field.’) wastes space and the reader’s time.
Step 3: Key skills and experience

- A very brief summary of your most relevant skills and experience. Employers or admissions officers scan CVs for 30 seconds or less before deciding if they want to read further. What should they know about you?
- Customize! For example, use ‘Key Marketing Skills & Experience’ for a marketing position.
- Use phrases instead of full sentences.
- For US applications capitalize first letter after bullet, for UK applications use small letter after bullet.
- Many companies and universities use computers to search for skills and experience that match their requirements. This is a good opportunity to include key words and phrases that the computer is looking for.
- See more samples of Key Skills and Experience in the CV examples.
Step 4: Education
- As a current student or recent graduate, you will probably want to put the education section next. Applicants who have a lot of work experience place that section before education in their CVs.
- Starting with your most recent education, list
- Your university degree or expected degree
- The full name of the university in English, location - city and country
- The period of time you have been there – month and year
- Main subject (US – major)
- Expected graduation date. If you are close to graduation and are quite sure of your final grade, you may want to include it here.
- Do not include grades unless they are above average
- You can list the grade in your main subject if it is higher
- See Grade Equivalents for converting German grades and other important information about grades
- Use standard English translations of degree titles, courses or exams. If there are none, write the German name and give the nearest equivalent in brackets
- Do not list anything earlier than Abitur or last results before entering university
- If you have received any academic honors, include them in this section
- At the end of the education section, list any additional training or courses that are relevant to the job or to understanding where you developed particular skills.
Step 5: Experience

- Using ‘Experience’ instead of ‘Work Experience’ enables you to include paid, and non-paid work, internships, volunteer work, and other experience that has helped develop your skill set. Employers care more that you have the experience rather than where you got it.
- Identify the employer or organization, the dates of employment (month/year), your position and your key responsibilities and accomplishments See The first steps to successful applications and interviews for how to identify and write about your accomplishments.
- Use reverse chronological order: Start with your most recent experience and work backwards.
- Use the present tense for current positions and the past tense for work you are no longer doing. See Grammar overview for CV-specific grammar help.
- Use action verbs to describe your responsibilities and accomplishments.
- Include any work-related recognition you have received at the end of this section.
Step 6: Additional skills
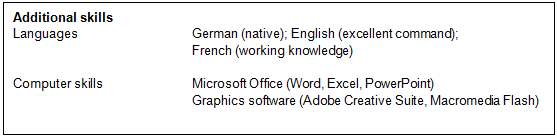
- List language skills starting with your native language(s), then in order of proficiency: see Describing language proficiency for the correct terms.
- Computer skills
- Any other relevant skills
Note: Skills that are particularly relevant for this job application should also be listed under Key Skills and Experience
Step 7: Interests and activities

- When work experience is limited, interests and activities can provide a way to show you’ve gained skills that relate to the position you are seeking.
- What you include also paints a picture of the kind of person you are.
- Volunteer activities are especially valued.
- Just writing a list of your activities doesn’t reveal much.
- Are any of your interests or activities particularly relevant to the job?
- Do any activities highlight your leadership, demonstrate responsibility and organizational ability or show long-term commitment?
- Sports imply good health and an active lifestyle and can also demonstrate teamwork and leadership skills.
- Memberships and your roles in organizations can be included in this section.
- Do not include religious or political activities. For example, if you do volunteer work for your church, write about the activity – ‘Volunteer football coach for 9 & 10 year-old boys’, ‘Led wilderness excursions for teen-age girls for three years ’.
- The term ‘hobbies’ doesn’t sound professional.
- Avoid ‘loner’ activities such as reading unless related to the job. The ever-popular ‘Meeting with friends’ may create a mental picture of clubbing and parties, prompting the recruiter to do a Facebook search.
Step 8: References

‘References available upon request’ is optional. It is understood that you will provide them when asked to do so. There is a great difference between the reference system in English- and German-speaking countries. In German-speaking countries it is common to ask for an open reference (i.e. you are able to see it in advance) which you can send with your job application. In English-speaking countries, if asked your referee will write a confidential reference which they will then send directly to the organisation you are applying to. However, before you give a name or names of referees you should always ask for their permission. For more information see Letters of recommendation.


